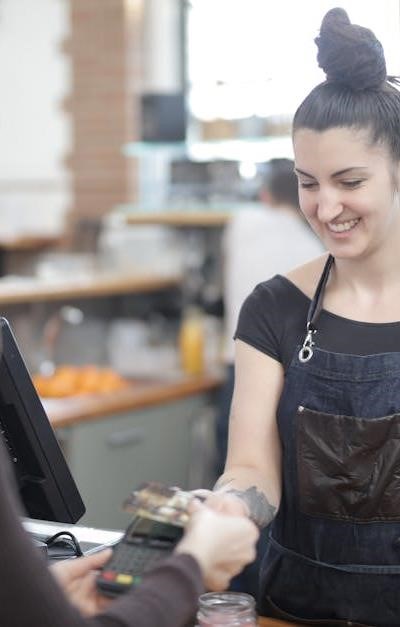

The world of payment processing is complex, offering diverse avenues for building a successful business․ Understanding the core models – from direct sales to reseller programs – is crucial․ This landscape involves merchant services, connecting businesses with acquiring bank capabilities․
You’ll encounter various players: ISOs (independent sales organizations), VARs (value-added resellers), and direct sales teams․ Each approach dictates your involvement in underwriting, credit risk assessment, and ultimately, building a robust merchant portfolio․
Success hinges on navigating credit card processing fees, understanding interchange rates, and offering solutions like POS systems, credit card terminals with EMV chip technology, and seamless online payments․ Consider bundled services to enhance value․
This overview will guide you through the key business models, helping you determine the best fit for your resources and ambitions within the evolving fintech and digital payments ecosystem, including Visa, Mastercard, and American Express․
Understanding the Core Components of the Ecosystem
At the heart of the payment processing ecosystem lies a network of interconnected entities․ The acquiring bank is fundamental, providing the financial infrastructure for merchant services and authorizing transactions․ ISOs (independent sales organizations) and direct sales teams act as intermediaries, sourcing merchants and facilitating the merchant account setup process․
Payment gateways are critical for e-commerce and online payments, securely transmitting data between the merchant’s website and the processor․ POS systems and credit card terminals, increasingly equipped with EMV chip technology, are essential for retail environments․ Understanding how these components interact is paramount․
Card brands – Visa, Mastercard, American Express – establish the rules and interchange rates governing transactions․ These rates, along with other credit card processing fees, directly impact merchant profitability․ Software integration via APIs allows for seamless connectivity between various systems․
Furthermore, fraud prevention measures and adherence to PCI compliance standards are non-negotiable․ The rise of mobile payments and subscription services adds layers of complexity, demanding adaptable solutions․ Finally, hardware sales and robust support services, including customer service, complete the picture, creating a holistic offering for merchants․
Choosing Your Sales & Service Delivery Model
Selecting the right sales and service model is pivotal for success․ Direct sales offer maximum control and potentially higher margins, but require significant upfront investment in personnel and infrastructure․ This involves building a dedicated sales team focused on prospecting and closing deals for merchant services․
Indirect sales, leveraging reseller programs and VARs (value-added resellers), expands your reach with lower initial costs․ However, it necessitates careful partner selection and management․ White label solutions allow partners to brand the services as their own, fostering stronger relationships․
Consider the level of support services you’ll provide․ Full-service models encompass everything from underwriting and risk management to fraud prevention and chargeback handling․ Alternatively, a more streamlined approach might focus solely on payment gateway provision and software integration․
Your target market – retail, e-commerce, or mobile payments – will also influence your choice․ Offering specialized POS systems or tailored online payments solutions can provide a competitive edge․ Don’t overlook the importance of API access for developers seeking custom integrations․ Ultimately, aligning your model with your capabilities and market demand is key․
Revenue Streams & Compensation Structures
Understanding revenue streams is fundamental to profitability․ The primary source is typically a markup on credit card processing fees, derived from the interchange rates set by card brands like Visa and Mastercard․ Transparent competitive pricing is crucial for attracting and retaining merchants․
Beyond processing fees, explore ancillary revenue opportunities․ Hardware sales – credit card terminals and POS systems – can contribute significantly․ Offering value-added services like PCI compliance assistance, fraud prevention tools, and dedicated customer service generates additional income․
Compensation structures vary widely․ Direct sales teams often operate on sales commissions, incentivizing performance․ ISOs and VARs frequently benefit from residual income based on the processing volume of their merchant portfolio․ Carefully consider the balance between upfront incentives and long-term revenue sharing․
Bundled services allow for premium pricing and increased customer loyalty․ Subscription services for software or advanced features provide recurring revenue․ For independent sales organizations, a tiered commission structure based on portfolio size and performance can motivate growth․ Accurate revenue forecasting and cost management are essential for sustainable success․
Future-Proofing Your Business: Growth & Innovation
Mitigating Risk & Ensuring Compliance
Operating within the payment processing industry demands a robust approach to risk management․ Chargebacks represent a significant threat; proactive fraud prevention measures are paramount․ Implement tools and strategies to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, minimizing financial losses and protecting your merchant portfolio․
PCI compliance is non-negotiable․ Ensure all merchants utilizing your merchant services adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)․ Offer guidance and support to facilitate compliance, reducing the risk of data breaches and associated penalties․ Regular security audits are highly recommended․
Thorough underwriting is critical․ Assess the credit risk associated with each potential merchant, evaluating their business model, financial stability, and processing history․ Implement clear guidelines for accepting or declining applications, minimizing exposure to high-risk businesses․
Stay abreast of industry trends and evolving regulations․ Compliance requirements are constantly changing; continuous monitoring and adaptation are essential․ Develop a comprehensive risk management plan that addresses potential threats, including data security, fraud, and regulatory violations․ Consider partnering with legal counsel specializing in fintech to ensure ongoing compliance․


A well-structured piece that effectively highlights the core components of the payment processing ecosystem. The emphasis on EMV chip technology and the need for secure payment gateways is spot on, given the current security landscape. I
This is a solid overview for anyone starting to explore the payment processing world. I particularly appreciate the breakdown of the different players – ISOs, VARs, direct sales – as it can be very confusing initially. My advice would be to really dig into the underwriting and credit risk aspects; that